Types of Abrasive Materials
March 07, 2023
Workpieces made of metal often contain natural impurities or defects that arise during the manufacturing or processing stages. These imperfections can complicate the application of coatings or hinder other critical processes, ultimately affecting the overall quality of the finished product.
Abrasives play a crucial role in removing unwanted materials and preparing the surface of the substrate for subsequent stages of production. This process involves propelling high-pressure water mixed with abrasives to eliminate dirt, oil, grease, chemicals, and other substances, achieving the desired finish.
Various types of abrasive materials, commonly referred to as media, are available for this blasting process, each offering unique benefits and drawbacks.
What Are the Different Types of Abrasive Media?
Let's take a closer look at the most common types of abrasive media, along with a brief description and their typical surface finishing applications:
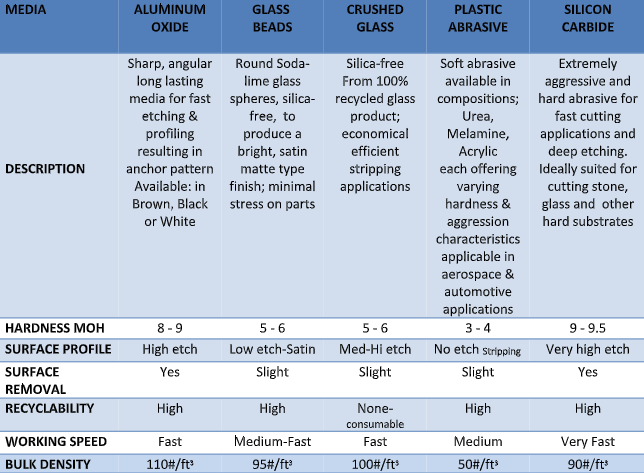
- Glass Beads: Glass is not as aggressive as other materials like steel shot or silicon carbide, but it is an excellent choice for applications requiring a softer, brighter finish. It works particularly well on stainless steel surfaces. Additionally, glass beads can be recycled multiple times, making them cost-effective for repeated use.
- Aluminum Oxide: Known for its superior hardness and strength, aluminum oxide is widely used in applications such as creating anti-slip surfaces, industrial blasting, and as a raw material in refractories. It is versatile enough to be used on nearly any substrate, including glass, granite, marble, and steel. Due to its ability to deeply etch surfaces, it is often employed in preparing surfaces before painting or applying coatings.
- Plastics: Plastic abrasives are dry thermoset cleaning media made from crushed urea, polyester, or acrylic. Each type comes in a range of hardnesses and particle sizes. Plastic is typically the preferred choice for mold cleaning, blasting plastic parts, or in situations where the substrate material must remain intact. Industries such as automotive, aviation, boating, electronics, and industrial sectors commonly utilize plastic media blasting.
- Silicon Carbide: As the hardest abrasive blasting material available, silicon carbide is ideal for demanding surface finishing tasks. It is available in various colors and purities, and its applications span bonded abrasive tools, lapping, polishing, glass etching, and general-purpose heavy-duty blast-cutting tasks.
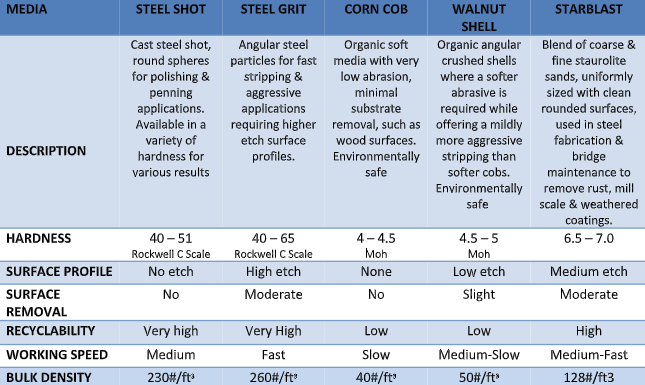
- Steel Shot & Grit: Steel abrasives are a cost-effective alternative to other abrasives due to their toughness and high recyclability. They can be used on a variety of surfaces to remove contaminants, create textures for proper coating adhesion, or in peening (hardening) applications. The correct size, hardness, and shape are crucial factors in selecting the right media.
- Starblast: Starblastâ„¢ is a mined loose blend of coarse and fine staurolite sands with extremely low levels of silica, making it an ideal general-purpose blasting abrasive. It is excellent for removing scale and corrosion from steel surfaces while maintaining low dust levels for better visibility.
- Walnut Shells: Walnut shell abrasive is a hard, naturally occurring material made from crushed walnut shells. It is the harder of the soft abrasives, available in various sizes for blast cleaning and polishing softer surfaces that could be damaged by harsher abrasives. Common applications include polishing soft metals, fiberglass, wood, plastic, and stone. It can also be used in tumbling operations for polishing gems and jewelry.
- Corn Cobs: Corn cob abrasive is a granular abrasive created by crushing the dense woody rings of corn cobs into different grit sizes. It is the softer of the naturally occurring abrasives, making it ideal for cleaning, deburring, burnishing, and deflashing applications. Industries such as jewelry, cutlery, engine parts, fiberglass, and graffiti or debris removal from wood, brick, or stone frequently use it.
The Evaluation Criteria
Each of these materials performs differently based on certain characteristics, which you should consider when making your selection:
- Hardness: Determined by the Mohs Hardness Scale, which rates materials from 1 to 10 based on their scratch resistance. A higher rating indicates the media is more likely to scratch the surface, an important consideration when working with softer substrates.
- Surface Profile: The abrasive's size, shape, hardness, and density collectively influence the profile it creates on the material’s surface. The outcome can range from no etch to a low, medium, or high etch.
- Surface Removal: When choosing an abrasive media, you need to know how much of the substrate's surface the material will remove to ensure the result aligns with the project's specifications.
- Recycling: If cost reduction is a priority for your business, consider whether the material can be recycled and reused after the blasting process.
- Working Speed: Some materials allow you to complete the blasting process faster than others, impacting productivity.
- Bulk Density: Measured in pounds per cubic foot, the abrasive's density affects its cleaning rate and the surface profile it leaves on the substrate.
Learn More About the Different Types of Abrasive Media
Finishing Systems offers several types of sandblast media for sale. Many of our products come in various grit sizes and packaging options to meet your company’s specific needs. All these materials provide the consistent quality and performance required to optimize your projects' outcomes.
Are you unsure about which abrasive media to choose? The Finishing Systems team has the experience and expertise to guide you through the decision-making process.
Contact us for more information or to get reliable answers to your abrasive media questions today.

In conclusion, understanding the properties and applications of various abrasive media is essential for selecting the right material for your specific needs. Whether you're dealing with delicate surfaces or demanding industrial applications, there is an abrasive solution tailored to your requirements. If you have any questions or need expert advice, don't hesitate to reach out to our team at Finishing Systems. We’re here to help you achieve the best results for your projects.
Ethylene Cracking Furnace Anchor
Anchors are mostly used as fixtures for integral linings (castable, plastic and sprayable linings). Refractory brick linings also use anchors, but they are not used in many occasions. Metal anchors are usually used to support and fix thin or heat-insulating integral linings, such as chimney linings, wear-resistant linings of petrochemical catalytic cracking reactors (usually tortoise shell mesh anchors), integral jet metallurgy The lining of the spray gun, the overall lining of the immersion pipe of the DH and RH vacuum degassing devices, the lining of the rotary kiln discharge day, the feeding port, etc. Metal anchors are mostly used to fix linings with a long-term use temperature below 1200 °C, or short-term use temperature above 1200 °C that can be used intermittently. Ceramic anchors are usually used to fix thicker (greater than 200mm) integral linings and are characterized by:
(1) It can withstand higher operating temperatures, and is generally used in the lining of kilns that are used for a long time above 1200 °C;
(2) It can withstand the erosion and corrosion of corrosive atmosphere;
(3) It can be extended to the working surface to reduce the peeling of the overall lining;
(4) Compared with metal anchors, the contact area with the refractory lining is large, so it has a greater supporting capacity;
(5) The thermal expansion coefficient is equivalent to that of the overall refractory material, which can eliminate the cracking or peeling of the lining due to thermal expansion mismatch
Ethylene Cracking Furnace Anchor,Corbel Anchor,601 Inconel Refractory Anchor,310 Stainless Steel Refractory Anchor
Puyu kiln technology (jiangsu) CO.,LTD , https://www.anchorpy.com


