Last Updated on July 21, 2023 Not all electric vehicle (EV) charging is created equal. One of the key distinctions among charging stations lies in their power output and how quickly they can recharge an EV. In essence, EV charging falls into three categories: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3. In general, the higher the charging level, the more powerful the output, and the faster it can charge your electric vehicle. Depending on the type of current they supply and their maximum power output, these stations are categorized accordingly. Levels 1 and 2 provide alternating current (AC), with maximum outputs ranging from 2.3 kW to 22 kW. On the other hand, Level 3 charging delivers direct current (DC) to the EV's battery, offering much higher power outputs, up to 400 kW. Table of Contents Electric vehicles (EVs) are more popular than ever before. Last year, over 10 million new EVs were sold globally, many of which were purchased by first-time buyers. One of the most significant changes in adopting electric mobility is the way we refuel our vehicles. Unlike traditional gas stations, EV charging locations are much more diverse, and the time it takes to charge depends on the type of charging station you use. This article breaks down the three levels of EV charging and explains the features of each level, including the type of current they supply, their power output, and the charging duration. EV charging is divided into three levels: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3. Generally speaking, the higher the charging level, the higher the power output and the faster it will charge your electric car. However, there are a few additional considerations. Before delving deeper into how each level functions, it's essential to understand how EV charging stations are powered. Without going too technical, there are two types of electrical currents, and which one is used plays a crucial role in EV charging: Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). The electricity that comes from the grid and is available through domestic outlets in homes and offices is always AC. This current is named after its flow pattern, which alternates periodically. Therefore, the current alternates direction. Since AC electricity can be transmitted over long distances efficiently, it is the global standard we all rely on daily. However, that doesn’t mean we don’t use direct current. In fact, we use it all the time to power electronic devices. The electricity stored in batteries or used in the internal circuits of electric devices is DC. Similar to AC, DC is named after its flow pattern; DC electricity moves in a straight line, providing your device with power directly. For reference, when you plug an electronic device into a socket, it always receives an alternating current. However, batteries in electric devices store direct current, so the energy must be converted at some point inside your device. When it comes to power conversion, electric vehicles follow the same principle. The AC power from the grid is converted inside the car by an onboard converter and stored in the battery as DC electricity—where it powers your vehicle. While Level 1 and Level 2 charging convert AC to DC via the vehicle's onboard converter, Level 3 charging supplies the battery with DC power directly. This is because the conversion from AC to DC happens outside the vehicle and within the charging station itself. Level 3 charging (also known as DC charging or fast charging) skips the relatively slow onboard conversion process, enabling exponentially higher power outputs and faster charging times. Below, we'll explore the differences between charging levels. Now that we understand the distinction between AC and DC and have established that Level 3 is undoubtedly the fastest, you might be wondering: How long does it take to charge an electric car per Level? This is the slowest (but most accessible) method of charging an electric car. Level 1 charging simply involves plugging the cable that came with your electric vehicle into a regular wall outlet. While this makes Level 1 charging usable nearly anywhere, it limits its power output to that of your home’s electrical circuit—typically 2.3 kW. Although charging times vary depending on the vehicle and other factors like weather conditions, driving style, and the onboard current converter, charging at Level 1 will replenish your EV’s battery with about 4 to 5 miles (6 to 8 kilometers) of range per hour. For instance, if you've driven 100 miles (160 kilometers), it will take you between 20 to 25 hours to recharge your vehicle. Due to its slow charging speeds and lack of specific protection beyond your home’s circuit breakers, Level 1 charging is discouraged for everyday EV charging and is only recommended as a last resort. Level 2 EV charging requires a dedicated charging station and is usually found in public or commercial parking spaces, workplaces, or residential areas. While still using alternating current, these charging stations are considerably faster than Level 1 charging. Level 2 charging stations are dedicated pieces of hardware wired directly into your home’s electrical circuit by a qualified professional. They offer relatively fast charging speeds and can include various smart functionalities. Roughly speaking, Level 2 charging is about 5 to 15 times faster than Level 1 charging, depending on the power output and the vehicle being charged. Charging for an hour with a 7.4 kW power output will add about 25 miles (40 kilometers) of range, 11 kW will add 37 miles (60 kilometers) of range, and 22 kW will add up to 75 miles (120 kilometers) of range. These calculations are approximations based on the average battery consumption of 18 kWh per 62 miles (100 kilometers). Actual power consumption depends on the vehicle, battery size, and vehicle conditions. Level 3 charging (DC) is significantly faster than Level 2 charging. Depending on the vehicle and the charging station’s power output, it can take between 15 minutes to an hour to charge most electric cars—making it quick and easy to charge on the go. Because the power output required for Level 3 charging stations is much higher than for Level 2 charging stations, Level 3 charging stations are better suited for commercial businesses like gas stations or service stops. You typically don’t see Level 3 charging stations installed at public parking locations or office spaces. Earlier, we explained that the battery inside an electric car only stores DC energy. This means that when using a Level 3 charging station, the conversion from AC (from the grid) to DC happens within the charging station itself. A Level 3 charging station is typically quite large because it needs to house powerful converters to handle the rapid conversion of AC power. Some Level 3 charging stations can deliver up to 400 kW of power, capable of charging up to 100 km in just 3 minutes. These large converters and high-power inputs also affect the charging rate. With Level 1 and Level 2 (AC) charging, the power is delivered steadily, representing a flat line. This is because the onboard converter of the EV is relatively small and can only take a certain amount of power at a time. With Level 3 charging, however, the charging rate quickly peaks before gradually slowing down. This is due to the battery’s ability to accept power, which decreases as it gets closer to full capacity. To illustrate this, imagine filling up an empty glass with water. When you start pouring water into the glass from a bottle, you allow it to flow quickly, but as you get closer to the top, you slow down to prevent overflow. Level 3 charging works similarly, with the empty glass representing the battery and the DC charging station as the bottle filled with water. This is why electric cars charge much slower once the battery is charged over 80 percent and why the final stretch of charging is always a bit slower. The differences between Level 1, 2, and 3 charging greatly impact how quickly you can fully charge your EV. Understanding how different charging levels work is important, but there are many other aspects of EV charging to consider that can affect your charging experience. Check out our comprehensive EV charging guide for an overview of everything you need to know about electric car charging, including where and how you can charge, how much EV charging costs, and other factors that influence charging times. Softgel Encapsulation Machine Accessory Equipment Softgel Encapsulation Machine Accessory Equipment,Oil Capsule Sealing Equipment,Softgel Encapsulation Machine Accessory,Softgel Encapsulation Machine Equipment ZHEJIANG FUCHANG MACHINERY CO., LTD. , https://www.fuchangmachinery.com

Boost Your EV Charging Knowledge
What Are the Different Levels of EV Charging?
How Are EV Charging Stations Powered?

Alternating Current vs. Direct Current
Alternating Current (AC)
Direct Current (DC)
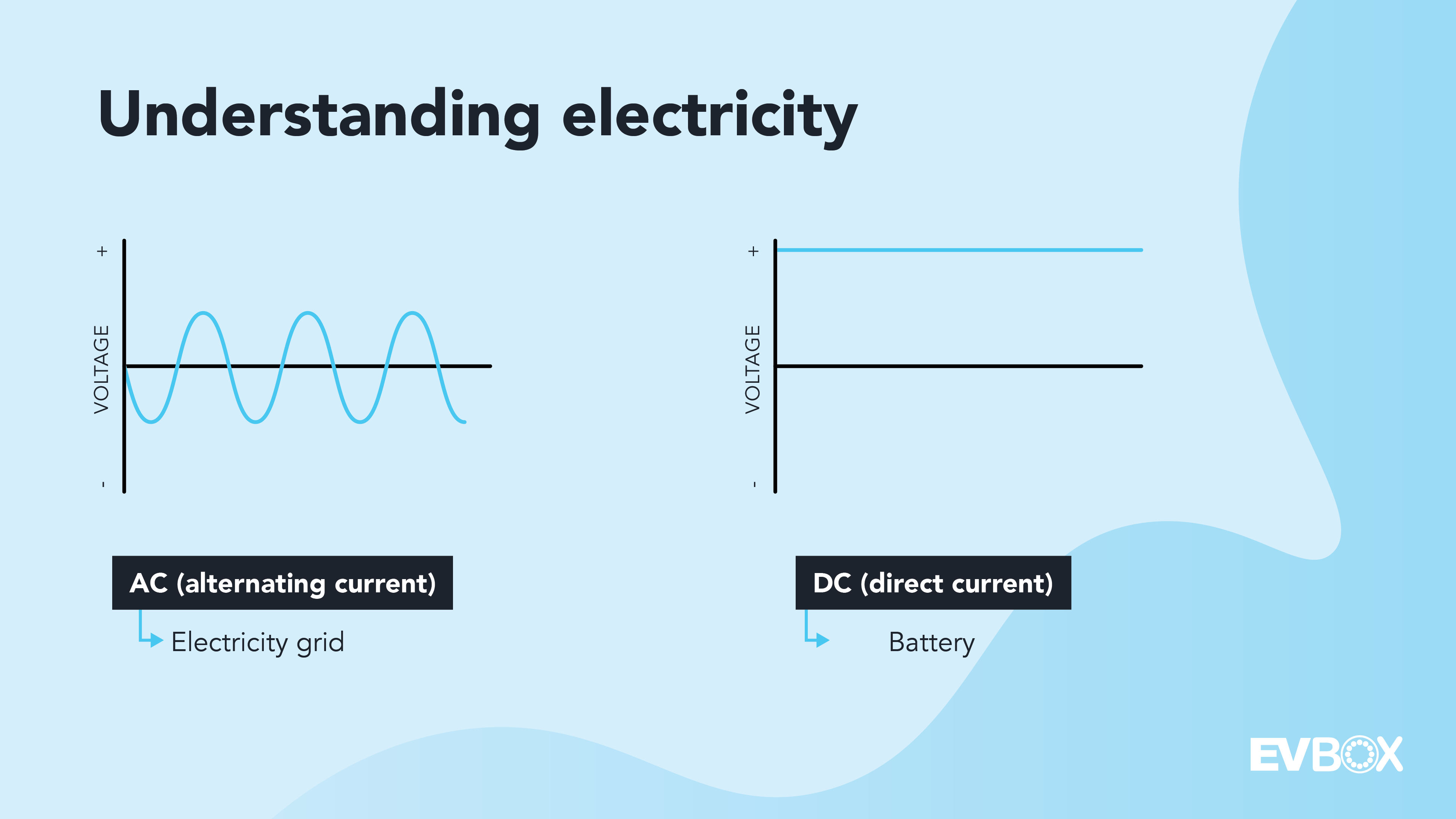
Which Type of Current Is Used to Charge My Electric Car?
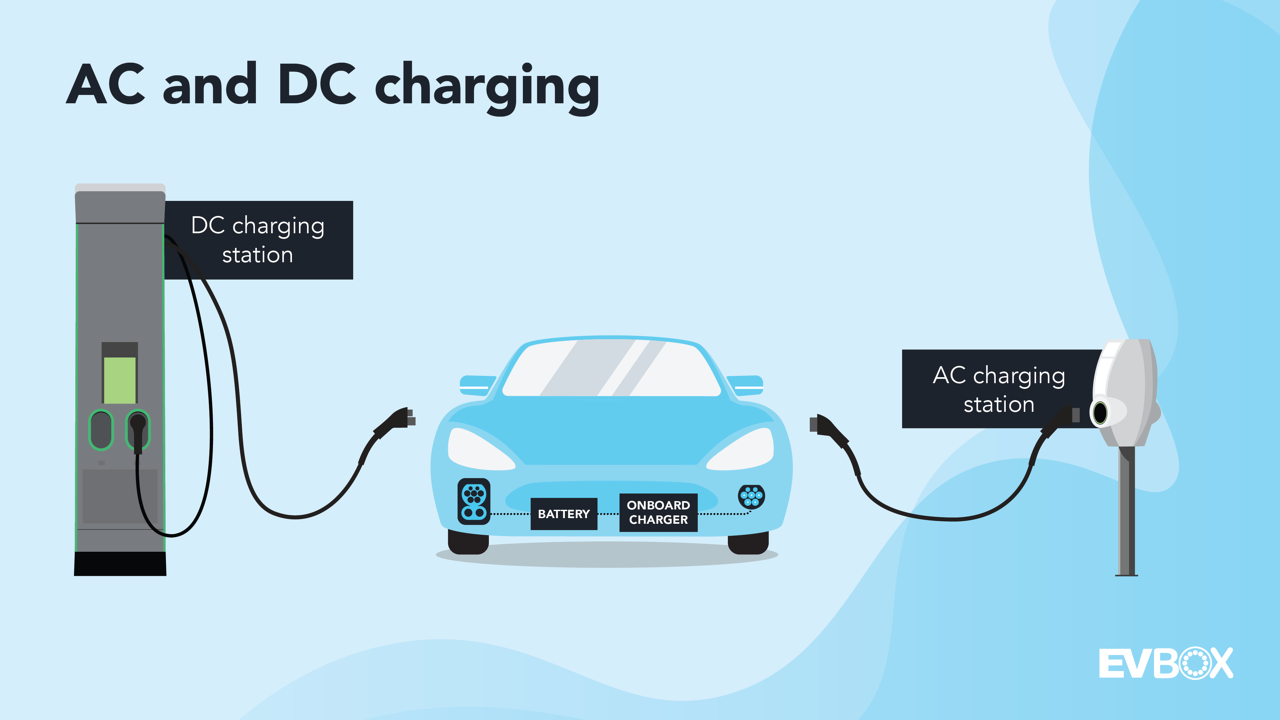
The Difference Between EV Charging Levels
Level 1, Level 2, Level 3 Average Charging Time Comparison
What Is Level 1 Charging?
How Does Level 1 Charging Work?

How Fast Is Level 1 Charging?
What Is Level 2 Charging?
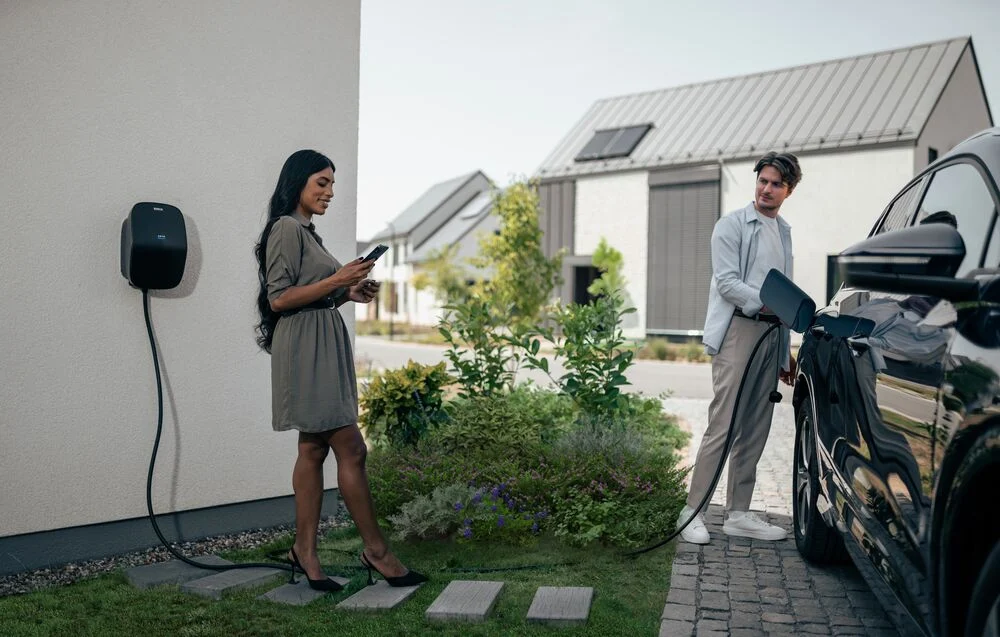

How Does Level 2 Charging Work?
How Fast Is a Level 2 Charger?
What Is Level 3 Charging?
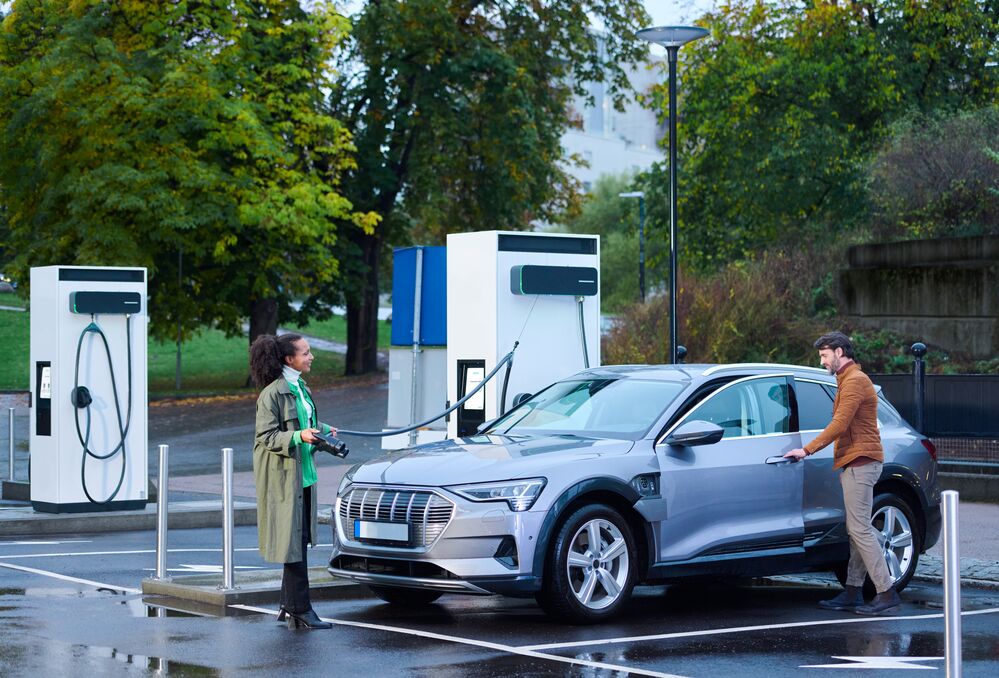

How Does Level 3 EV Charging Work?
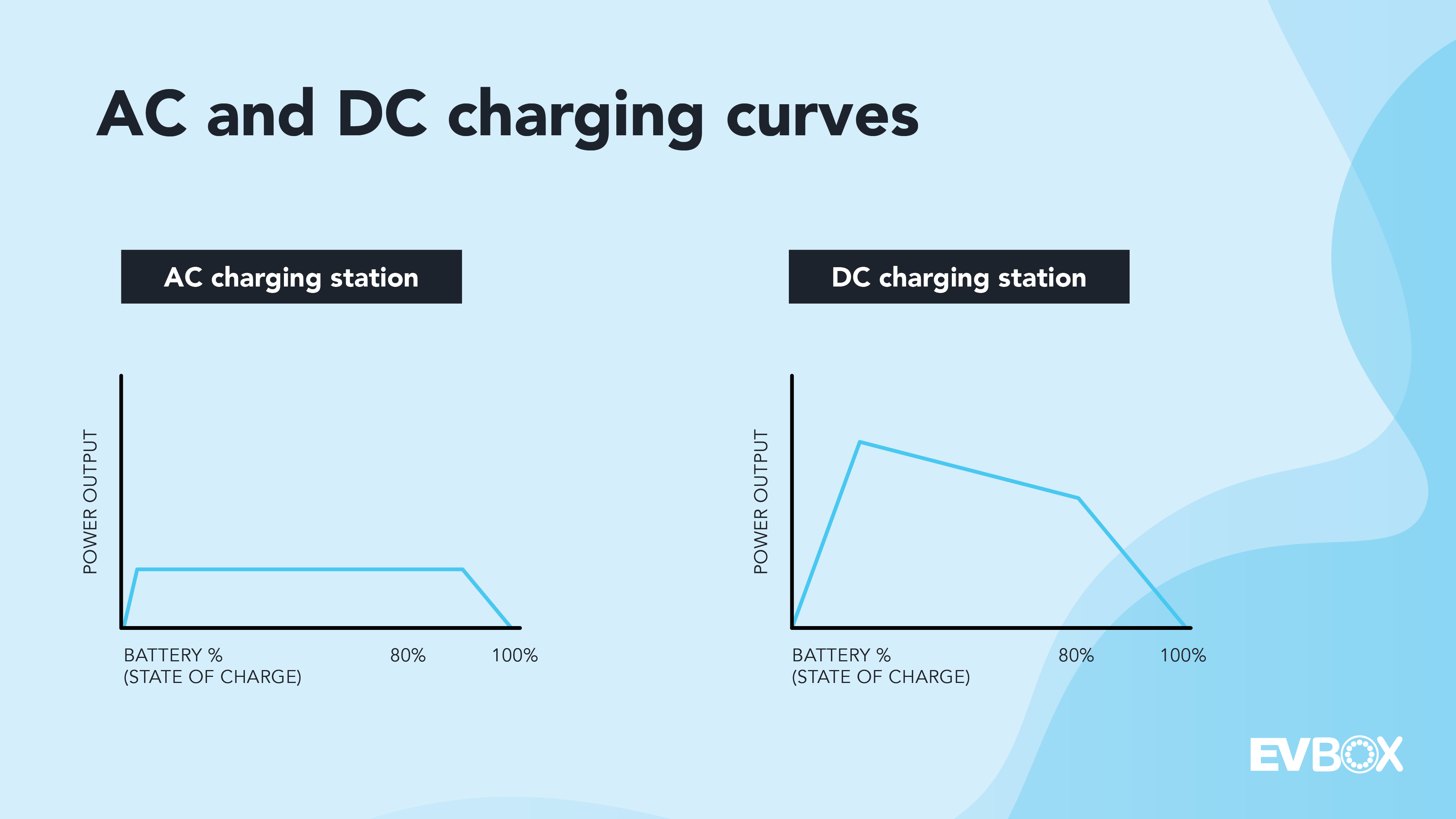
Why Does Level 3 Charging Flow Differently?
Learn More About EV Charging
EV charging levels explained [2023 update]
Last Updated on July 21, 2023 Not all electric vehicle (EV) charging is created equal. One of the key distinctions among charging stations lies in their power output and how quickly they can recharge an EV. In essence, EV charging falls into three categories: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3. In general, the higher the charging level, the more powerful the output, and the faster it can charge your electric vehicle. Depending on the type of current they supply and their maximum power output, these stations are categorized accordingly. Levels 1 and 2 provide alternating current (AC), with maximum outputs ranging from 2.3 kW to 22 kW. On the other hand, Level 3 charging delivers direct current (DC) to the EV's battery, offering much higher power outputs, up to 400 kW. Table of Contents Softgel Encapsulation Machine Accessory Equipment Softgel Encapsulation Machine Accessory Equipment,Oil Capsule Sealing Equipment,Softgel Encapsulation Machine Accessory,Softgel Encapsulation Machine Equipment ZHEJIANG FUCHANG MACHINERY CO., LTD. , https://www.fuchangmachinery.com