Solar Panel Cleaner Machine,Solar Plate Cleaning Machine,Panel Cleaning Machine,Solar Plate Washing Machine Taian Longye Import And Export Trade Co.,ltd , https://www.drillingrigfactory.comPixel Resolution
The pixel resolution of an image refers to the total number of pixels that make up the image. This is typically expressed in terms of the number of columns and rows, like 1920 x 1080, or simply as the total number of megapixels, such as 2.1 MP (1920 x 1080 = 2.07 million pixels).
Let’s take a look at the pixel resolutions of the Elios 1 and Elios 2:
While the pixel resolution gives us a sense of how large the image is, it doesn't tell us much about how large an object appears in the image or the level of detail that can be observed. For those insights, we need to look at metrics like ground sampling distance (GSD) and spatial resolution.
---
Elios 1 Pixel Resolution
FHD Video
1920 x 1080
2.1 MP
Elios 2 Pixel Resolutions
FHD Video
1920 x 1080
2.1 MP
4K Video
3840 x 2160
8.3 MP
Photo
4,000 x 3,000
12 MP
Ground Sampling Distance (GSD)
The ground sampling distance (GSD), expressed in mm/px, is the distance between the centers of two adjacent pixels on the observed object. A GSD of 1 mm/px means each pixel on the image corresponds to 1 mm in the real world. A smaller GSD implies that objects appear larger in the image and finer details become visible.
Unlike pixel resolution, GSD depends on the distance between the camera and the subject. As the camera gets closer to the objects, the GSD improves (i.e., it becomes smaller). With a fisheye lens, the GSD also varies depending on the position of the object within the image. Objects near the center of the image have a smaller GSD (appear larger), while objects in the corners have a higher GSD (appear smaller).
Here’s a visual example:
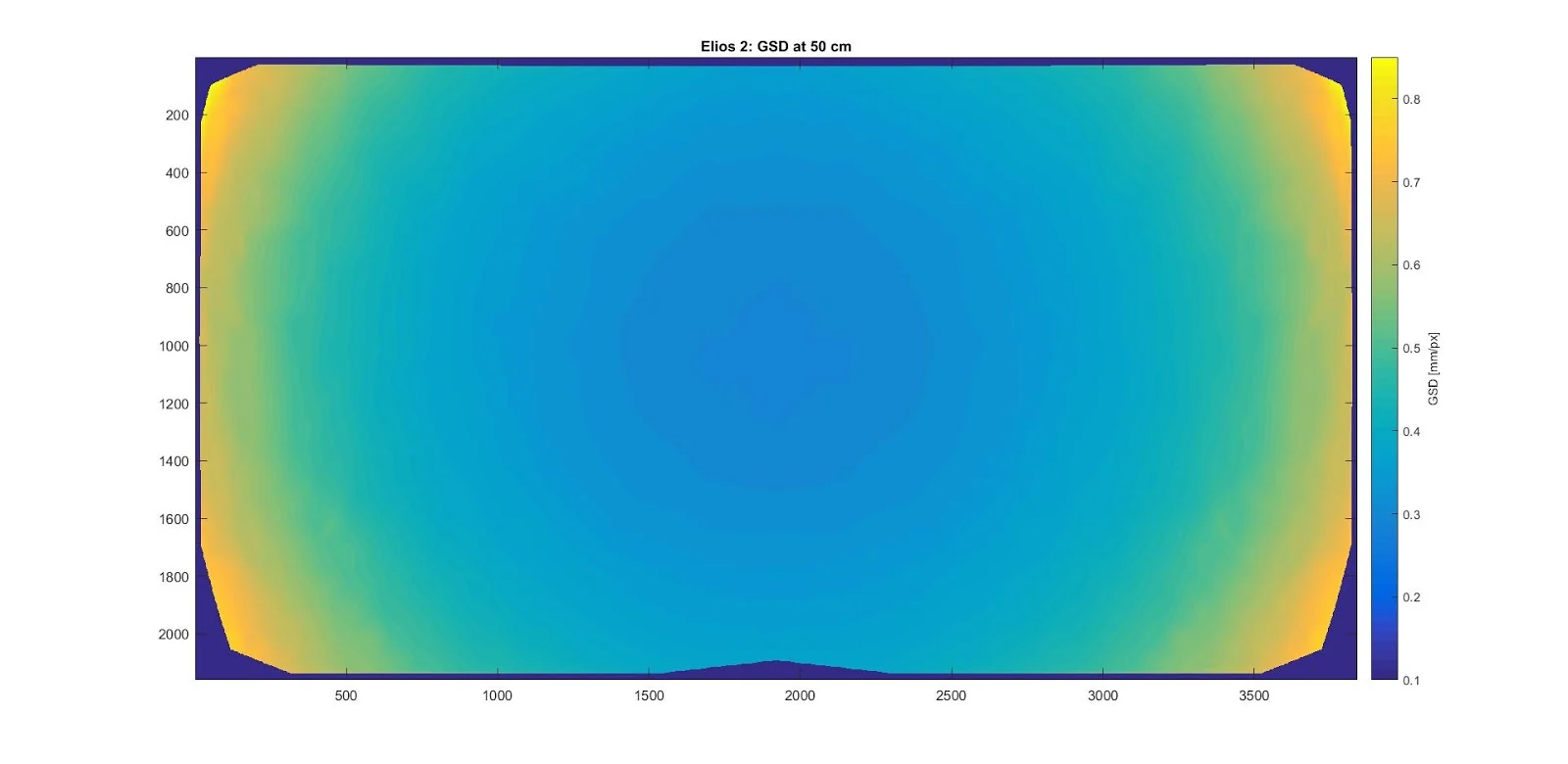
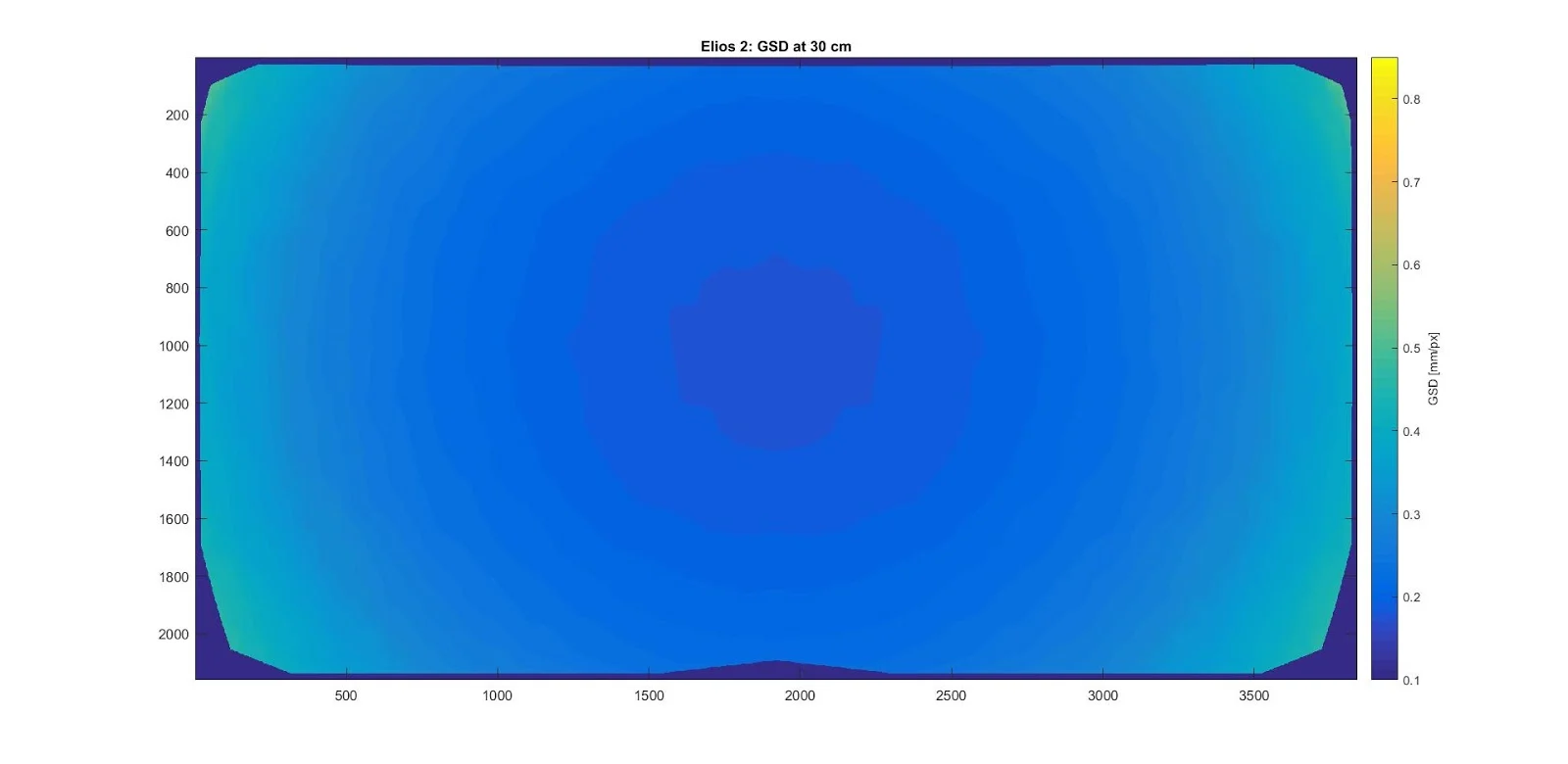
*This figure shows how the GSD changes across the image when the Elios 2 faces a flat vertical wall. The data was obtained by automatically measuring the size of a regular grid pattern on the wall.*
GSD is particularly important for photogrammetry and measurements in images. However, it doesn’t fully describe the ability to detect and characterize objects or defects in the image.
For instance, consider two images captured by the same camera at the same distance. Both images have identical pixel resolution and GSD. However, if one image suffers from poor lighting—forcing the camera to use a high ISO or long exposure—the resulting image will have more noise or motion blur, reducing the level of detail visible.
---
Spatial Resolution
The spatial resolution, or angular resolution, measures the smallest details that can be seen in the image. Unlike theoretical GSD, spatial resolution considers additional factors such as blur, image noise, contrast, and post-processing techniques like compression, denoising, and edge sharpening. Therefore, spatial resolution is the best metric to evaluate the ability to detect and characterize objects in an image.
Spatial resolution is often expressed in "line pairs per millimeter" (lp/mm). This unit describes alternating black and white line patterns.
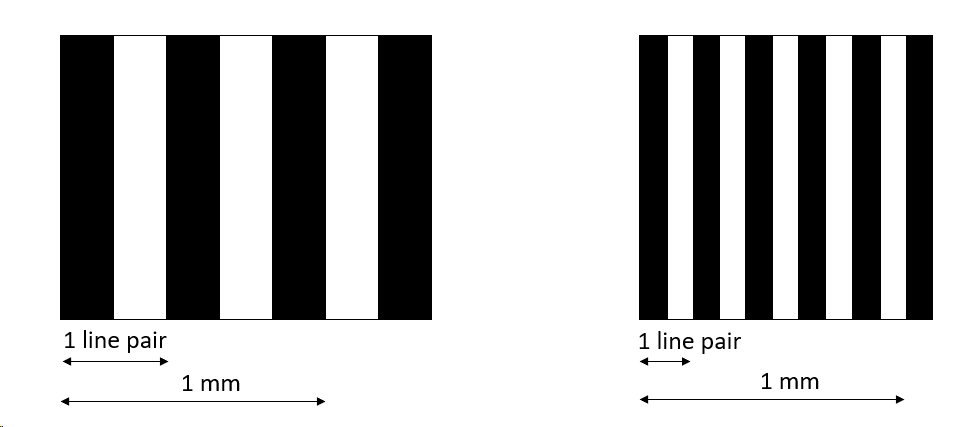
*Left: Pattern with a frequency of 2.5 lp/mm. Right: 5 lp/mm*
A spatial resolution of 2 lp/mm means that a pattern with two cycles per millimeter (two black and two white lines) can be distinguished in the image. A pattern with a higher frequency will appear gray, blending black and white lines, and won’t be resolved.
Here’s an example of a spatial resolution test:
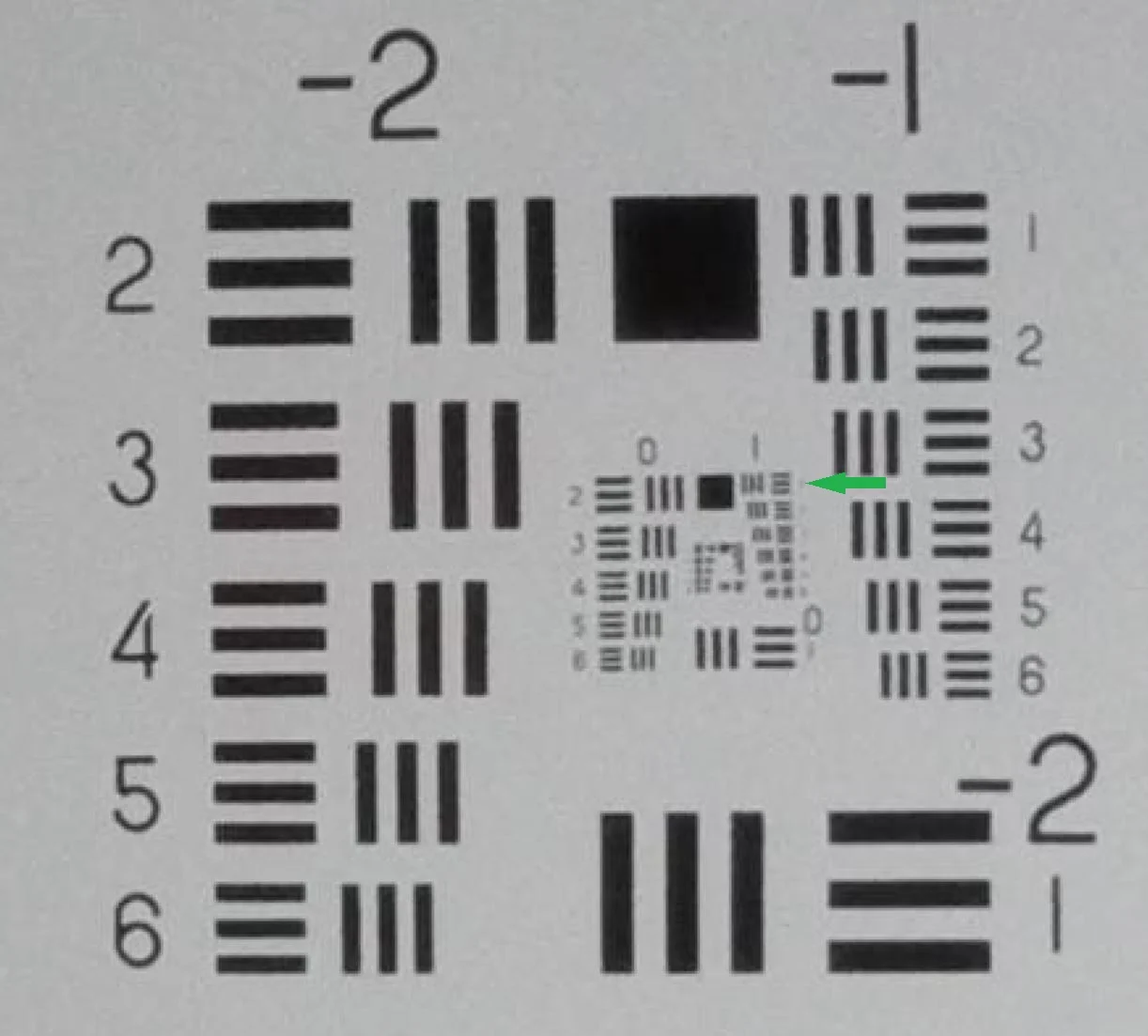
*Snapshot of an image taken by Elios 2 (4K video) at 300 mm from a USAF 1951 resolution chart. The smallest resolved element is Element 1, Group 1 (indicated by the green arrow). In Element 2 (below), the contrast begins to drop significantly, and individual lines cannot be distinguished.*
Spatial resolution tends to be better in the center of the image than on the edges, where lens quality is lower. Additionally, spatial resolution is an isotropic property—it can vary depending on whether the line pattern is vertical or horizontal.
Spatial resolution also depends on the camera's focus distance and depth of field. For Elios 2, the highest spatial resolution is achieved when the object is 15 to 30 cm away from the camera. If the object is too close, it will appear larger (lower GSD), but it will be out of focus and blurry, reducing spatial resolution.
To achieve the best spatial resolution, it’s critical to understand the minimum distance allowed by the camera’s focal length and maintain that distance during data capture. To assist pilots, Elios 2 features a distance lock function and Cockpit (the app for controlling Elios 2) displays the drone-to-object distance and GSD (in mm/px). Spatial resolution is also indicated via a color-coded scale, as shown below:
Keep in mind that small screens can mask image blur because the image is downscaled to fit the screen resolution. With Elios 2, you might be tempted to fly at 15–20 cm without noticing the blur, but remember that your 4K footage will look sharper and clearer if you stay at 30 cm.
Other factors that improve spatial resolution and overall image quality include:
- Adequate lighting to keep the camera’s ISO low and exposure times short.
- A stable drone to minimize motion blur.
- A clean camera lens—fingerprints and smudges make images blurry and can cause glare!
---
Distance
Color
Meaning
> 40 cm
Â
White
Flying closer will improve spatial resolution
30 to 40 cm
Â
Green
High spatial resolution and sharp image
20 to 30 cm
Â
Orange
Highest spatial resolution—but the image becomes blurry
< 20 cm
Â
Red
The image is extremely blurry. Spatial resolution decreases.
Beyond Resolution
While spatial resolution is a key metric for assessing image quality and detecting objects during inspections, other factors are equally important:
- Lighting techniques.
- Colors (contrast, white balance, etc.).
- Ability to observe from multiple angles.
- Quality of the display screen.
These elements extend beyond mere camera resolution and must be addressed holistically by the entire Unmanned Aerial System (UAS). Elios 2’s compact size and collision tolerance allow it to access objects and observe them from various angles. Its advanced lighting system enhances the perception of 3D details, making it easier to spot cracks, holes, or irregularities. These features contribute significantly to Elios 2’s ability to detect and characterize objects of interest.
With practice, you’ll improve your piloting skills and focus more on data capture than navigation. Keeping these concepts in mind will greatly enhance the quality of your footage.
Different industries have varying requirements for image quality. If you’ve experimented with different tools or have feedback about Elios 2’s image quality, feel free to reach out!
Drones Camera Resolution: Three Metrics You Should Know About
In this article, we’ll delve into three crucial metrics for describing the resolution of a drone camera. To clarify these concepts, we'll refer to the cameras of the drones we’re most familiar with—specifically, the Elios 1 and Elios 2.
---